What is Six Sigma and How is it Applied?
Six Sigma is a data-driven management methodology that aims to improve quality by minimizing errors and variability in processes. This approach, first developed by Motorola and adopted by large companies such as General Electric, uses statistical methods to control variation in processes and aims to increase customer satisfaction. The basic philosophy of Six Sigma is to prevent errors in processes and optimize operations through continuous improvement. This methodology uses a five-step cycle known as DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) to measure, analyze, improve and control process performance.
The implementation of Six Sigma requires a detailed analysis of the existing processes of the business. First, the processes requiring improvement are identified and project objectives are set. Then, data on process performance is collected and analyzed to identify root causes. In the improvement phase, recommendations are developed and tested to solve problems in the processes and the most effective solutions are implemented. Finally, process improvements are sustained and process performance is continuously monitored. Six Sigma provides significant advantages to businesses and increases customer satisfaction by reducing error rates, increasing efficiency and lowering costs.
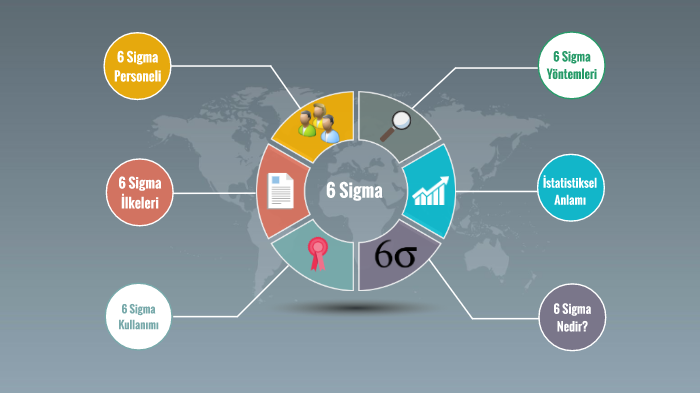
What is Six Sigma?
Six Sigma is a method that aims to improve quality by minimizing errors and variability in processes. It was first developed by Motorola in the 1980s and later adopted by large companies such as General Electric. Six Sigma uses statistical methods to control variation in processes and aims to increase customer satisfaction. The term “sigma” is a statistical unit that measures the error rate or variability of performance in a process. The Six Sigma level targets a defect rate of 3.4 defects per million, which means an almost perfect level of quality. The basic philosophy of Six Sigma is to prevent defects and optimize processes through continuous improvement. This methodology makes business processes more efficient, reducing costs and providing a competitive advantage.
Principles and Tools of Six Sigma
Six Sigma is structured around the DMAIC cycle (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control), which consists of five basic principles. These principles ensure that process improvement projects are carried out systematically and successfully.
Define
Six Sigma projects start with the definition phase. At this stage, processes requiring improvement are identified and the scope of the projects is clarified. Project objectives are defined in line with customer needs and expectations. Furthermore, the project team is formed and roles are distributed.
Measure
In the measurement phase, the current process performance is evaluated and the error rates in the process are determined. Data is collected and information is obtained about the current state of the processes. This phase helps identify opportunities for improvement and key performance indicators (KPIs) are defined.
Analyze
In the analysis phase, the data is analyzed in detail and the root causes of the process are identified. This stage is critical for understanding the causes of errors in processes and identifying potential areas for improvement. Using statistical analysis and graphical tools, factors affecting the performance of processes are identified.
Improve
In the improvement phase, recommendations are developed and implemented to solve problems in the processes. This phase involves finding innovative solutions to optimize processes and increase efficiency. Improvement proposals are tested and the most effective solutions are implemented.
Control
In the control phase, the sustainability of the improvements in the processes is ensured and the performance of the processes is monitored. This stage ensures that the improvements are permanent and that the processes continue in accordance with the set standards. Control plans are created and process performance is continuously monitored.
Implementation of Six Sigma
The implementation of Six Sigma starts with analyzing the current state of the business. This analysis helps to identify error rates in processes and areas requiring improvement. Six Sigma projects are usually initiated with the support of top management and adopted throughout the organization.
Project Selection and Planning
Six Sigma projects should align with strategic objectives and focus on areas that will create the most value for the business. In the project selection phase, improvement opportunities are identified and the scope of projects is clarified. Project plans are created and targets are set. In addition, project teams are formed and team members receive the necessary training.
Data Collection and Analysis
In the data collection phase, the necessary data is collected to obtain information about process performance. This data provides information on the current state of processes and helps identify opportunities for improvement. After the data is collected, it is examined in detail during the analysis phase. Using statistical analysis and graphical tools, the root causes affecting the performance of processes are identified.
Improvement and Implementation
In the improvement phase, recommendations are developed and implemented to solve problems in the processes. This phase involves finding innovative solutions to optimize processes and increase efficiency. Improvement proposals are tested and the most effective solutions are implemented. During the implementation of improvement recommendations, the performance of the processes is continuously monitored and necessary corrective measures are taken.
Continuous Monitoring and Control
In the control phase, the sustainability of the improvements in the processes is ensured and the performance of the processes is monitored. This stage ensures that the improvements are permanent and that the processes continue in accordance with the set standards. Control plans are created and process performance is continuously monitored. Deviations in processes are identified and necessary corrective measures are taken.
Benefits of Six Sigma
Six Sigma brings many benefits to businesses. These benefits include reducing error rates in processes, increasing efficiency, reducing costs and increasing customer satisfaction.
Reducing Error Rates
Six Sigma improves quality by minimizing error rates in processes. This increases customer satisfaction and gives the business a competitive advantage. In addition, reducing error rates in processes helps to reduce costs.
Increasing Productivity
Six Sigma enables optimizing processes and increasing efficiency. This improves the performance of the business and ensures competitive advantage. Furthermore, increasing the efficiency of processes helps to reduce costs and increase profit margins.
Reducing Costs
Six Sigma reduces costs by reducing waste in processes. This increases the profit margins of the business and supports sustainable growth. In addition, reducing costs increases the competitive advantage of the business.
Increasing Customer Satisfaction
Six Sigma aims to increase customer satisfaction. This is achieved by responding quickly and efficiently to customer demands. Increasing customer satisfaction increases customer loyalty and builds long-term customer relationships.
Six Sigma is a data-driven methodology that aims to improve quality by minimizing errors and variability in processes. This approach ensures optimized processes and increased customer satisfaction. Six Sigma is structured around the DMAIC cycle, which consists of five basic principles: define, measure, analyze, improve and control. These principles ensure that process improvement projects are carried out systematically and successfully. The implementation of Six Sigma consists of analyzing the current state of the business, data collection and analysis, improvement and implementation, and continuous monitoring and control. Six Sigma brings many benefits to businesses: reducing defect rates, increasing productivity, lowering costs and improving customer satisfaction. These benefits increase the competitive advantage of businesses and support sustainable growth. Six Sigma is critical for businesses that want to succeed in today’s competitive business world.